Ethernet passive optical networking (EPON) and gigabit passive optical network (GPON) are variations of PON. EPON and GPON were developed by the IEEE and ITU-T to enable gigabit rate solutions to deliver Ethernet and IP services. This article will discuss the difference between EPON and GPON.
EPON VS. GPON
The difference between EPON and GPON can be illustrated from the following aspects.

Data Rate
EPON is defined by IEEE 802.3 standard, ratified as 802.3ah-2004 for 1.25 Gbps (1.0 Gbps before 8B/10B coding) and IEEE 802.3av standard for 10Gbps (10G-EPON). The upstream and downstream data rate of EPON is symmetrical.
GPON supports a variety of data rate levels including asymmetric uplink and downlink rates, downlink 2.5Gbps or 1.25Gbps, uplink 1.25Gbps or 622Mbps. Users can choose the upstream and downstream data rate based on their needs, making it more flexible than EPON.
Split Ratios
EPON supports a minimum split ratio of 1:32, also it can support higher split ratios of 1:64, and 1:128. Providers can define the split ratio according to the services and bandwidth they want to support. GPON supports split ratios of 1:32, 1:64, and 1:128. It offers a multiplicity of split ratios, but the cost advantage is not obvious. EPON can deploy cheaper optics at the ONU as it does not need to reach a split ratio of 128.
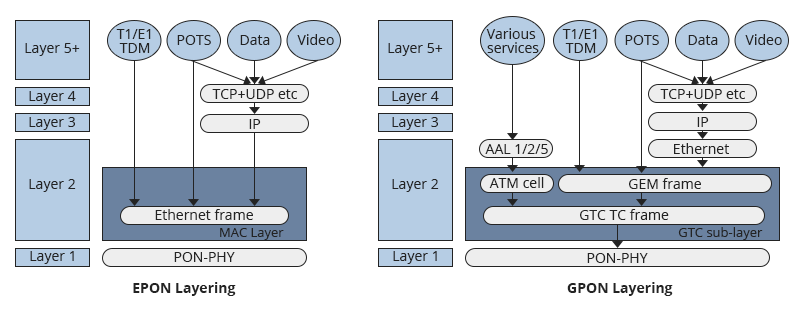
Layering
EPON has a simple networking architecture. It directly uses an Ethernet frame to transmit data, voice, and video.
GPON has two layers. First, TDM and Ethernet frames are wrapped into GEM frames. Secondly, ATM cells and GEM frames are encapsulated into the GTC frame and delivered via PON.
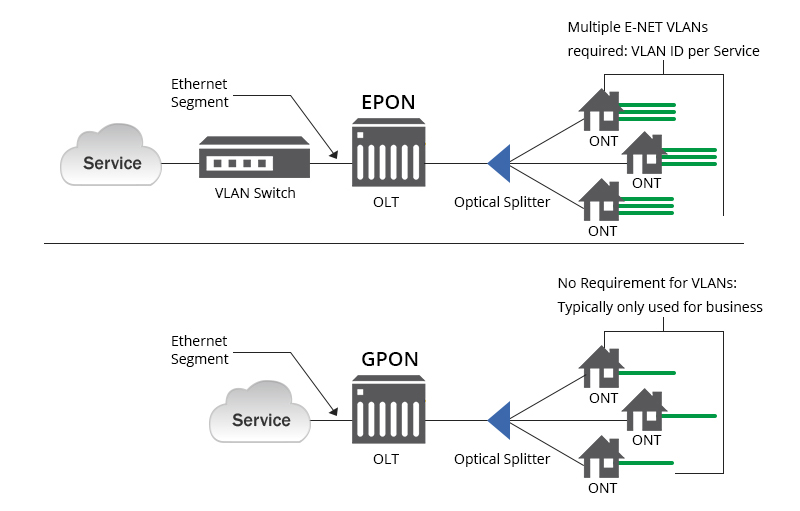
Quality of Service (QoS)
GPON has inherent QoS full service, while EPON requires the extra cost of manually configuring the virtual local area network (VLAN) label to enable QoS.
Operation Administration and Maintenance (OAM)
GPON uses three types of control messages: OMCI (ONT management and control interface), OAM, and PLOAM (Physical Layer OAM). Each message control channel performs its duties to achieve full OAM security management.
EPON only has simple OAM functions, such as FEF (far-end fault), loop-back, and monitoring.
Costs
The cost of EPON and GPON relies on the OLT, ONU/ONT, and passive optical components. For the same number of users, the cost for the fiber and cabinet with EPON is similar to GPON. The cost of OLT and ONT is decided by the ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit) and optical transceiver modules. The GPON chipsets available in the market are based on FPGA (field programmable gate array), which is more expensive than the EPON MAC (media access control) layer ASIC. Moreover, the optical module of GPON is more expensive than EPON.
Conclusion
In performance, GPON is better than EPON. It is more suitable for users who require high bandwidth, triple-play multi-service, QoS, security, and ATM backbone network. In contrast, it would be better to choose EPON for those who pay more attention to the cost and less security. Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if any needs.


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products




 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products





 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China