Optical fiber networks operate on different passive optical network (PON) standards. A PON is a network system specific to fiber technology that delivers broadband network access to homes or businesses. One of many PON standards is GPON. This article will provide some knowledge about GPON.
What is GPON?
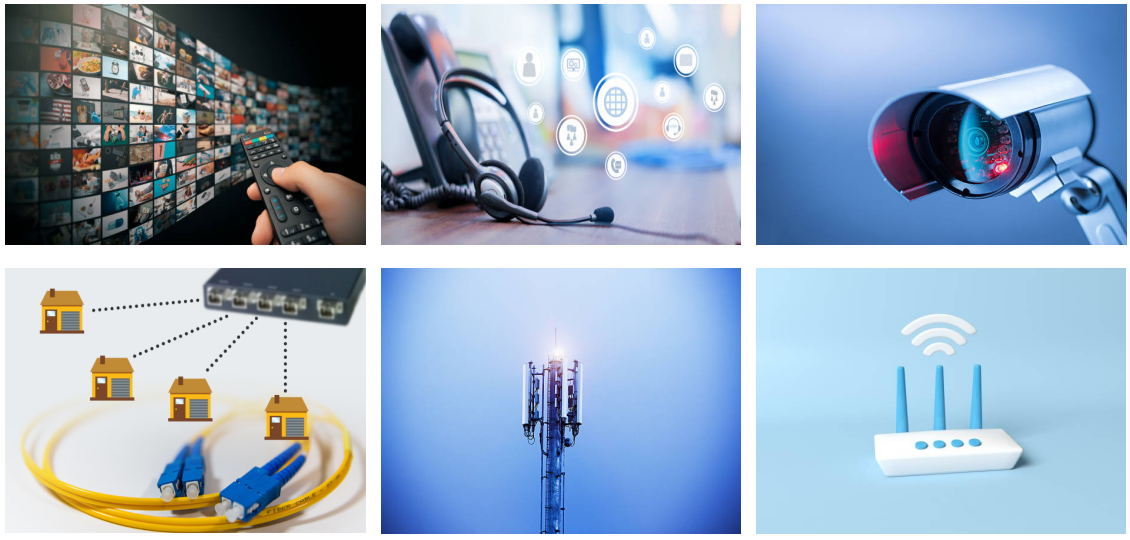
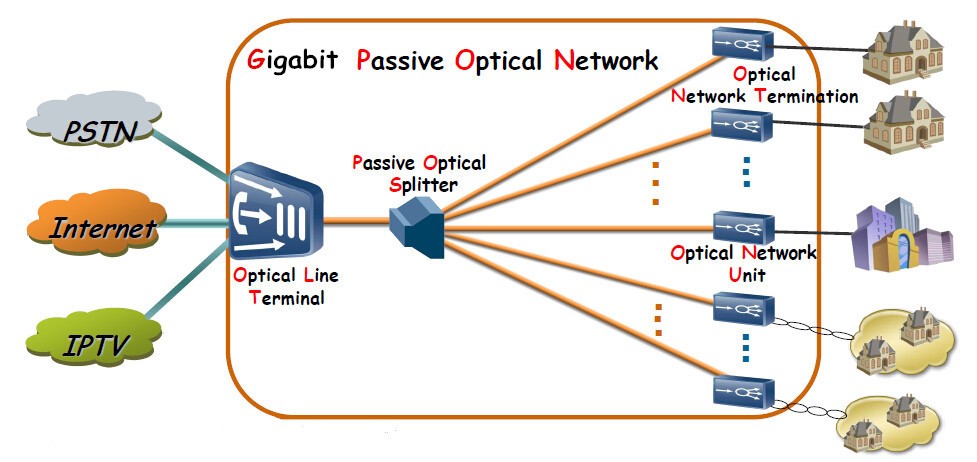
Gigabit passive optical network (GPON ) is a point-to-multipoint access network. Its main feature is to use passive splitters in the fiber distribution network (ODN), enabling one single feeding fiber from the provider’s central office to serve multiple homes and businesses. In addition, GPON uses an IP-based protocol and asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) encoding to integrate voice and data traffic on the same network.
Components of GPON
There are three main components of GPON: optical line terminal (OLT), optical fiber splitter, and optical network terminal (ONT).
1. OLT
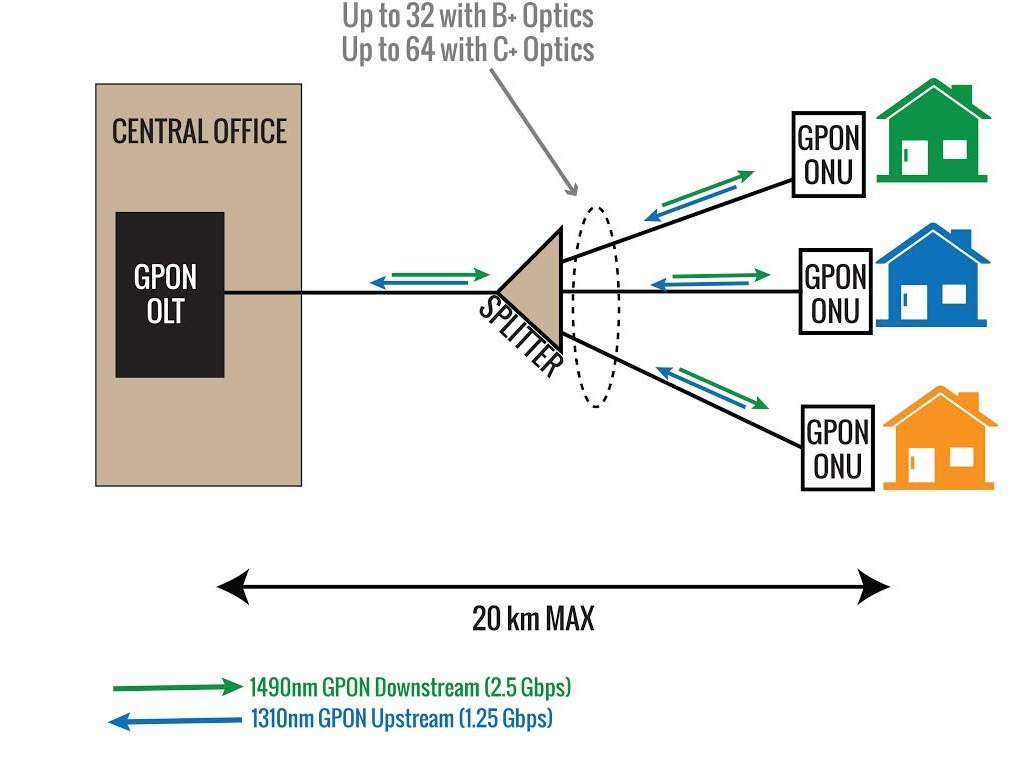
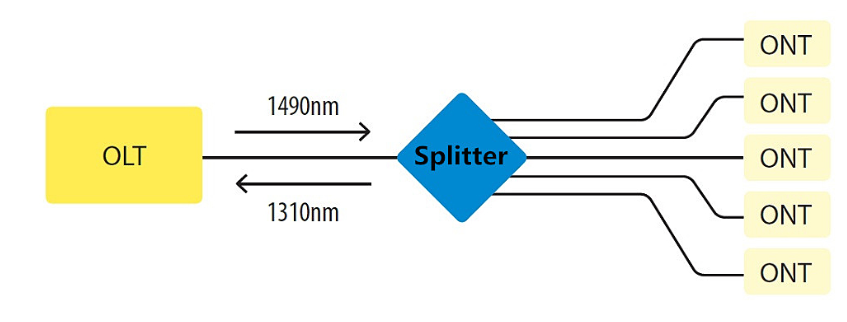
OLT is a device that serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network. It is an active ethernet aggregation device that is located in a data center or the main equipment room. An OLT converts the optical signals to electrical signals and presents them to a core ethernet switch. The OLT replaces multiple layer 2 switches at distribution points. OLT distributing signal is connected with backbone cabling or horizontal cabling through optical splitters, which are connected to the optical network terminal at each work area outlet.
2. Optical Fiber Splitter
The optical fiber splitter is an integrated waveguide optical power distribution device that can split an incident light beam into two or more light beams and contain multiple input and output end. A GPON splitter often has a specified split ratio that could be 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, and 1:64, depending upon the number of outputs required. The most common splitters deployed in a GPON system are uniform power splitters with a 1xN or 2xN splitting ratio, where N is the number of output ports.
3. ONT
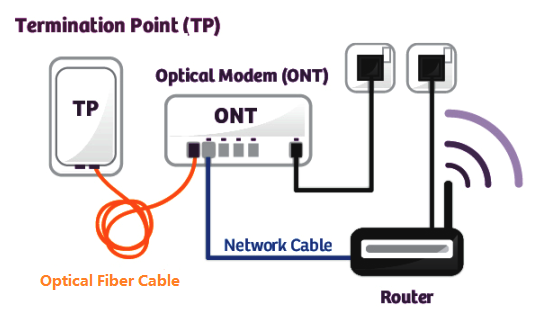
ONT also called the modem, connects to the termination point (TP) with an optical fiber cable, and connects to the router via a LAN / Ethernet cable. It converts the optical signals to electrical signals to deliver to the end device. ONT always has multiple Ethernet ports for connection to IP services such as CPUs, phones, wireless access points, and other video components.
Benefits of GPON
GPON has the benefits of high bandwidth, high security, low cost, easy installation, longer life, long-distance transmission, space-saving, energy-saving, scalable, and future-proof solutions.
Applications
GPON is used in data, video on demand, IPTV, VoIP, CATV, CCTV, FTTH, FTTB, FTTC, FTTD, FTTO, FTTM, FTTW, D-CCAP, etc.
Conclusion
GPON is a future-proof solution for providing broadband services. It provides high bandwidth, low cost, and long-distance transmission. Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if any needs.


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products



 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products





 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China