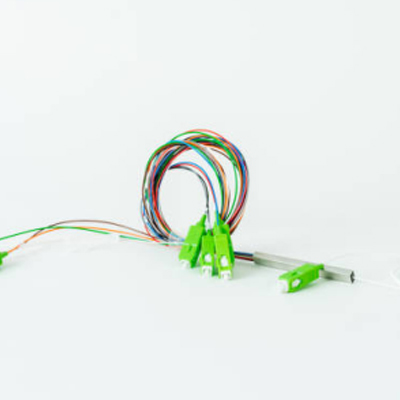
A fiber optic splitter is an optical passive device that can split or separate an incident light beam into two or more light beams. In terms of working principle, fiber optic splitter can be divided into FBT (fused biconical taper) splitter and PLC (planar lightwave circuit) splitter. There are lots of differences between PLC splitter and FBT splitter, which is confusing for many users. This article will explain the differences between the FBT splitter and the PLC splitter.
FBT VS. PLC Splitter
A difference between the FBT splitter and the PLC splitter can be illustrated from the following aspects.
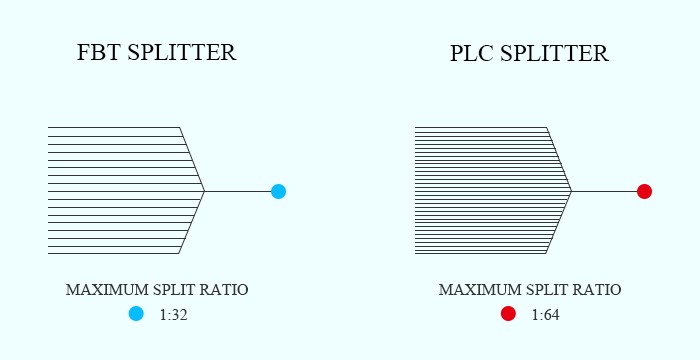
1. Splitting Ratio
The splitting ratio is decided by the inputs and outputs of a fiber optic splitter. The maximum split ratio of the FBT splitter is up to 1:32, which means one or two inputs can be split into an output maximum of 32 fibers at a time. While the split ratio of the PLC splitter is up to 1:64 - one or two inputs with an output maximum of 64 fibers. Besides, the FBT splitter is customizable, and the special types are 1:3, 1:7, 1:11, etc. But the PLC splitter is non-customizable, and it has only standard versions like 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64, etc.
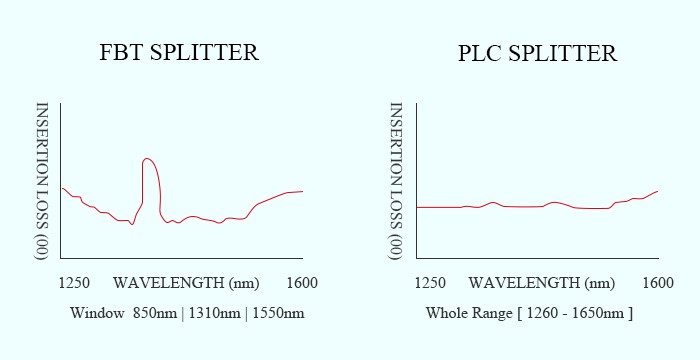
2. Operating Wavelength
FBT splitter only supports three wavelengths: 850nm, 1310nm, and 1550nm, which makes it inability to work on other wavelengths. The PLC splitter can support wavelengths from 1260 to 1650nm, and the wavelength can be adjusted to support more applications.
3. Asymmetric Attenuation Per Branch
The signal processed by the FBT splitter cannot be split evenly due to a lack of management of the signals, so its transmission distance can be affected. PLC splitter can support equal splitter ratios for all branches, which can ensure a more stable optical transmission.
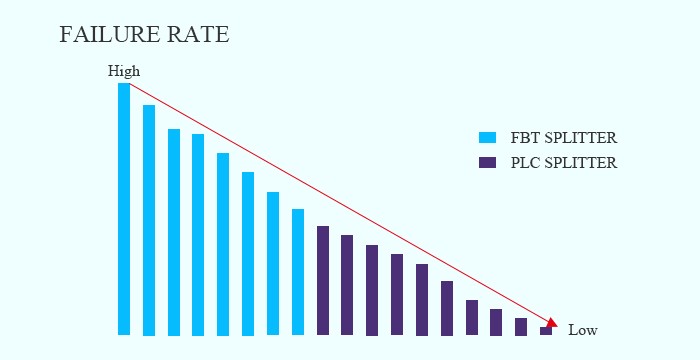
4. Failure Rate
FBT splitter is used for networks requiring the splitter configuration of fewer than 4 splits. The larger the split, the greater the failure rate. When its splitting ratio is larger than 1:8, more errors will occur and cause a higher failure rate. Thus, the FBT splitter is more restricted to the number of splits in one coupling. But the failure rate of the PLC splitter is much smaller than the FBT splitter.
5. Temperature Dependent Loss
Temperature-dependent loss (TDL) of the splitter is affected by the manufacturing process and the sensitivity of the device. Once the working temperature of the splitter is out of range, insertion loss will increase and influence the performance of the splitter. FBT splitter can only work at -5 to 75 ℃ and PLC splitter can work at the temperature of -40 to 85 ℃.
6. Cost
Owing to the complicated manufacturing technology of a PLC splitter, its cost is higher than the FBT splitter. If your application is simple and short of funds, the FBT splitter can provide a cost-effective solution.
Conclusion
Overall, the PLC splitter has better performance and fewer limitations, but the FBT splitter is less expensive to save more for the budget. Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if any needs.


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products


 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products



 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China